Digital financial services now sit at the center of how customers interact with banks and fintech apps.
Users expect to store funds, send money, and track transactions without leaving the platform they already use.
Meeting those expectations requires more than a payment gateway. It requires a wallet layer that can manage balances, identities, and compliance in real time.
This is where digital wallet API integration becomes important. Instead of building complex wallet infrastructure from scratch, you can connect your app to a secure wallet engine through APIs.
That connection allows your team to focus on user experience while the underlying system handles ledger accuracy, transaction processing, and regulatory requirements.
For your business, the goal is not only to launch faster. The goal is to launch with confidence, knowing the platform can scale, stay compliant, and support new services over time.
A well-planned wallet API integration creates that foundation and helps you deliver reliable financial features inside your own app.
This blog will help you learn how to integrate digital wallet APIs into your app without the research hassle or confusion.
Let’s get into it with the meaning!
What Is a Digital Wallet API?
A wallet API for fintech connects your application to a regulated wallet engine. It manages user balances, transaction history, and account controls through secure endpoints. It also links to identity, fraud monitoring, and reporting systems.
Many teams confuse wallets with payment gateway APIs. A gateway moves money between accounts. A wallet stores value and manages financial identity.
Here is the difference in simple terms.
| Feature | Digital Wallet API | Payment Gateway API |
|---|---|---|
| Stored balance | Yes | No |
| P2P transfers | Yes | No |
| Remittances | Yes | Limited |
| User accounts | Yes | No |
| Compliance layer | Built-in | Partial |
This is why mobile wallet API integration plays a much bigger role in product architecture than simple checkout processing.
💡Expert Tip
Common Business Use Cases for Wallet API Integration
You do not implement wallets for the sake of technology. You implement them to unlock revenue models and customer retention.
And so each use case shapes the type of fintech API integration you need. Some of the most common business use cases for wallet API integration are:
| Use Case | Required APIs |
|---|---|
| Remittance App | Wallet, FX, Payout, KYC |
| Neo-bank | Wallet, Card, Compliance |
| Merchant App | Wallet, QR, Settlement |
| Super App | Wallet, Payments, Loyalty |
Remittance App
A remittance platform needs wallet accounts to hold sender funds before payout.
And FX and payout APIs connect the wallet to international corridors. Plus, strong KYC and AML integration ensures regulatory compliance across borders.
Neo-bank
A neo-bank uses wallet infrastructure as the core account layer.
Card issuing and compliance APIs connect the wallet to everyday banking services. This setup supports real-time balances, transaction history, and regulatory reporting.
Merchant App
Merchant platforms use wallets to manage customer balances, refunds, and settlements.
QR and payment APIs enable in-store and online acceptance. Plus, settlement tools ensure funds move correctly to merchant bank accounts.
Super App
A super app combines multiple services in one ecosystem.
Wallet APIs support payments, peer transfers, and loyalty credits in a single balance view. This model improves user retention and increases transaction frequency across services.
Digital Wallet API Architecture Overview
Before you start coding, you need a clear view of the wallet backend architecture. Wallet systems operate in layers. Each layer has a clear responsibility.
The key layers of a wallet API architecture are:
| Layer | Role |
|---|---|
| App Layer | User experience |
| API Layer | Secure communication |
| Wallet Core | Ledger & balances |
| Compliance Layer | KYC, AML, Monitoring |
| Integration Layer | Banks, cards, payouts |
Here’s the breakdown of each layer:
App Layer: This is the front-end your customers interact with. It shows balances, transaction history, and payment options in a simple interface.
API Layer: This layer acts as the secure bridge between your app and the wallet engine. It manages authentication, request validation, and encrypted data exchange.
Wallet Core: The wallet core is the financial engine of the system. It maintains the ledger, updates balances in real time, and records every transaction accurately.
Compliance Layer: This layer supports KYC and AML integration along with transaction monitoring. It ensures your wallet operations align with regulatory requirements.
Integration Layer: This connects the wallet platform to external financial systems. It links to banks, card networks, payout providers, and other payment rails.
This layered model supports fintech platform scalability. You can update the front end without touching the ledger and add corridors without rewriting compliance logic.
Here’s the expanded step-by-step section written for banks, fintechs, and financial institutions, with a clear, practical flow.
The DigiPay.Guru Architecture:
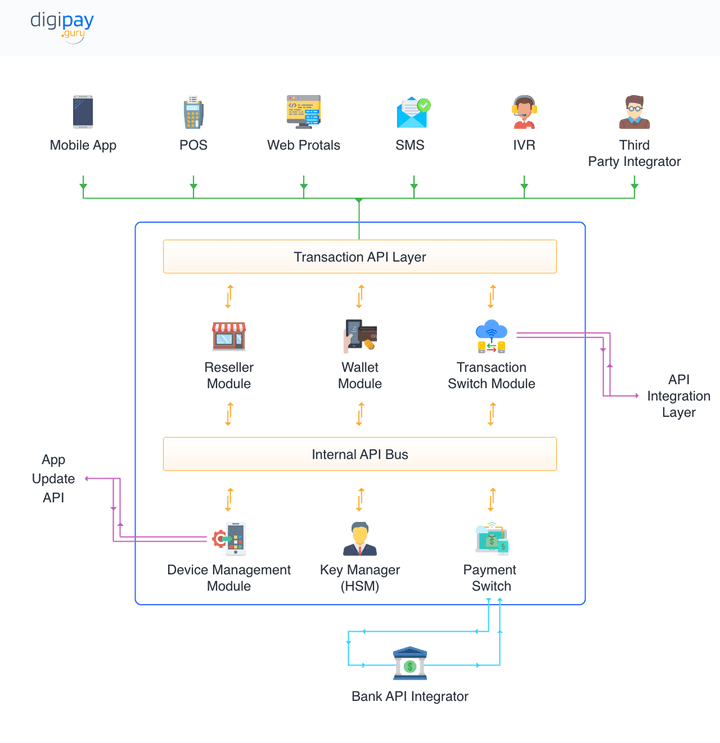
Step-by-Step: How to Integrate Digital Wallet APIs into Your App
A successful digital wallet API integration follows a structured process. Each step reduces risk and improves long-term scalability. Skipping steps often leads to compliance gaps, technical rework, and delayed launches.
The key steps are:
Step 1: Define Business and Regulatory Scope
Start with your product model and target markets.
A wallet used for domestic payments has different requirements than one supporting cross-border remittances. Plus, regulatory obligations, reporting standards, and licensing conditions must be clear before any technical work begins.
This step aligns your wallet infrastructure for fintech with legal and operational realities. It prevents costly redesigns after development has already started.
💡Expert Tip
Step 2: Choose the Right Wallet API Provider
Your provider becomes part of your financial infrastructure.
Evaluate their:
-
Ledger capabilities
-
Compliance coverage
-
Uptime history, and
-
Scalability readiness.
Strong documentation and sandbox access are essential for smooth onboarding. Look for a secure wallet API built for regulated environments.
Plus, a mature provider reduces your technical burden and helps you meet compliance expectations faster.
Step 3: Set Up API Authentication and Security
Security configuration comes before feature integration. Set up token-based authentication, encryption keys, and access controls for every system that interacts with the wallet APIs.
This ensures transaction data remains protected and traceable. Proper authentication also supports audit requirements and fraud monitoring from day one.
Step 4: Integrate Core Wallet Features
Now you connect user profiles in your app to wallet accounts. This includes APIs for account creation, balance checks, transaction history, debit, and credit operations.
Also, accurate real-time balance updates are critical for trust. And strong ledger system prevents reconciliation errors and reduces operational disputes.
Step 5: Implement KYC, AML, and Compliance Workflows
Wallets must operate within a clear wallet compliance framework.
-
Integrate identity verification before wallet activation.
-
Connect transaction monitoring systems to detect unusual activity.
-
Automated reporting tools should support regulatory submissions.
Embedding compliance early reduces risk and ensures smooth audits later.
Step 6: Connect External Financial Systems
Your wallet does not operate in isolation. Integrate it with banks, card networks, payout partners, and other financial rails through the integration layer.
This step enables funding, withdrawals, settlements, and cross-border flows. Reliable integrations also ensure your wallet supports real-world financial operations at scale.
Step 7: Test in Sandbox and UAT Environments
-
Before launch, simulate real transaction volumes and failure scenarios.
-
Test reconciliation, reporting accuracy, and system response times under load.
-
User Acceptance Testing confirms that product, compliance, and technical teams align.
-
Thorough testing reduces launch risk and supports long-term fintech platform scalability.
Each of these steps builds on the previous one. Together, they create a stable and compliant foundation for mobile wallet API integration that can grow with your institution’s digital strategy.
Build In-House vs Use a White-Label Digital Wallet API
Many teams consider building wallet systems internally. This path looks flexible on paper, but becomes complex in practice. The build vs buy digital wallet debate often comes down to time and risk.
| Factor | Build In-House | White-Label Wallet API |
|---|---|---|
| Time to market | 12–18 months | 6–8 weeks |
| Compliance effort | Very High | Included |
| Cost | High upfront | Predictable |
| Scalability | Custom | Built-in |
| Regulatory risk | High | Lower |
A white label digital wallet API reduces engineering load and compliance exposure. Your team focuses on product innovation instead of regulatory maintenance.
💡Expert Tip
Security & Compliance Considerations in Wallet API Integration
Security and compliance define long-term success. Regulators expect strong controls regardless of company size. Wallet systems must produce audit trails and enforce monitoring rules.
| Area | Client | Wallet API Provider |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure security | ❌ | ✅ |
| KYC workflows | Shared | ✅ |
| AML monitoring | ❌ | ✅ |
| Regulatory updates | ❌ | ✅ |
Infrastructure Security
The wallet provider is responsible for securing servers, databases, and network layers. This includes encryption at rest, encryption in transit, and access control at the infrastructure level.
KYC Workflows
Identity verification is typically a shared responsibility. Your institution defines onboarding policies, while the wallet platform enables verification checks and document validation tools.
AML Monitoring
Transaction monitoring systems detect unusual patterns and flag suspicious activity. A strong wallet engine automates these checks to reduce manual review and regulatory exposure.
Regulatory Updates
Financial regulations evolve frequently. A mature wallet API provider updates compliance logic and reporting frameworks to reflect new rules, thereby reducing operational strain on your internal teams.
This structure ensures your wallet platform operates within a defined wallet compliance framework, supports audit readiness, and protects both your customers and your institution.
Scalability & Performance Considerations
Growth introduces new pressures. More users mean more transactions. More markets mean more compliance variations. Your wallet infrastructure for fintech must adapt smoothly.
| Challenge | Wallet API Capability |
|---|---|
| High TPS | Distributed ledger |
| Multi-country | Config-based rollout |
| Compliance changes | Rule engine |
| New features | Modular APIs |
This design allows feature expansion without platform instability. It supports global rollout without rebuilding systems.
💡Expert Tip
How DigiPay.Guru Simplifies Digital Wallet API Integration
Choosing a wallet partner is not just a technical decision. It is an operational and regulatory decision.
Banks and fintechs like yours need a platform that reduces complexity, shortens launch timelines, and supports long-term expansion.
This is where DigiPay.Guru focuses its approach.
| Aspect | DigiPay.Guru | Custom Build |
|---|---|---|
| Go-live speed | Fast | Slow |
| Compliance | Built-in | Manual |
| Support | 24/7 | Internal |
| Expansion | Easy | Complex |
Go-live Speed
DigiPay.Guru provides ready-to-integrate wallet APIs and a pre-built ledger system. So, your team connects through documented endpoints instead of building financial infrastructure from the ground up. This shortens deployment cycles and reduces engineering strain.
Compliance Built-In
The platform includes a structured wallet compliance framework with support for KYC, AML monitoring, and reporting. Instead of designing compliance workflows from scratch, your team configures rules based on your regulatory environment.
24/7 Support
Wallet operations run continuously, not just during office hours. Dedicated technical and operational support 24*7 helps resolve issues quickly and keeps your services stable as transaction volumes grow.
Easy Expansion
As your business enters new markets or adds services, the modular wallet infrastructure for fintech allows feature rollout without reengineering the core. This supports regional expansion, new payment rails, and higher transaction volumes with less disruption.
DigiPay.Guru’s approach aligns with API-first fintech platforms that treat wallets as financial infrastructure rather than front-end features. That structure allows your institution to focus on customer experience while the platform manages ledger integrity, compliance logic, and system scalability.
Conclusion
Modern financial apps are no longer judged only by features. They are judged by how reliably they handle money. A stable wallet layer ensures that balances are accurate, transactions are traceable, and compliance requirements are consistently met.
That is why digital wallet API integration is a strategic infrastructure decision, not just a technical task.
For banks and fintechs, the advantage of a well-integrated wallet is long-term flexibility. You can introduce new services, enter new markets, and support higher transaction volumes without reworking your core systems.
Moreover, a strong wallet foundation reduces operational strain while keeping your platform aligned with regulatory expectations.
If you are planning to launch or modernize wallet capabilities, choosing the right platform makes a measurable difference.
Great news is - DigiPay.Guru’s digital wallet solution is built to support secure integration, compliance readiness, and scalable growth to help your institution deliver dependable financial experiences today and adapt confidently for tomorrow.

FAQs
A digital wallet API connects your app to a secure wallet system that manages balances, transactions, and user accounts. It acts as the bridge between your front-end experience and the financial ledger behind it.
These APIs also link to compliance, security, and reporting tools. This allows institutions to offer stored value and payments without building infrastructure from scratch.
Integration timelines depend on scope, compliance requirements, and internal readiness. With a mature wallet platform, core integration can take a few weeks rather than many months.
Pre-built compliance and ledger systems reduce development time significantly. Proper planning and sandbox testing help accelerate deployment.
Yes, when implemented using a secure, enterprise-grade wallet platform. Strong encryption, token-based authentication, and audit logs protect transaction data. Built-in monitoring also helps detect suspicious activity. Security must be designed into the integration from the start, not added later.
Yes, wallet APIs can support cross-border transfers when combined with FX and payout integrations. The wallet manages the sender’s balance while connected services handle currency exchange and settlement.
Compliance layers ensure KYC and AML checks are applied across corridors. This enables regulated remittance services inside your app.
Most institutions choose to buy due to compliance complexity and faster time to market. Building in-house requires deep fintech expertise and ongoing regulatory maintenance. A proven wallet platform reduces risk and operational burden. This allows teams to focus on customer experience and innovation.
An in-house build offers control but demands significant time, budget, and compliance resources. A white-label wallet platform provides ready infrastructure with built-in security and regulatory support.
It shortens deployment timelines and reduces technical debt. For most banks and fintechs, the white-label route is more practical.
The main risks include weak security architecture, incomplete compliance workflows, and poor scalability planning. Integration without proper ledger design can cause reconciliation issues. Ignoring regulatory reporting can lead to penalties. Choosing an experienced wallet provider reduces these risks significantly.
A modular wallet backend supports higher transaction volumes and new services without reengineering. It allows expansion into new markets through configuration rather than full redevelopment. Scalable infrastructure also improves system stability during growth. This protects both performance and customer trust over time.
Leaders should expect built-in KYC verification, AML transaction monitoring, and audit-ready reporting. The platform should support regulatory updates and configurable compliance rules. Clear logs and traceability are essential for audits. Compliance must be embedded into operations, not managed manually.
With a ready wallet platform, institutions can launch in months rather than years. Timelines depend on licensing, integrations, and internal approvals. Pre-built APIs and compliance modules reduce development cycles. Proper planning ensures faster go-live without compromising security or regulation.
DigiPay.Guru offers a modular wallet and remittance platform with built-in compliance and scalable architecture. Institutions benefit from faster deployment, reduced regulatory burden, and reliable infrastructure.
The platform supports regional expansion and new service rollout with minimal disruption. This makes it a practical partner for long-term digital financial growth.