Even though the world is transforming digitally, there are still areas that are untapped and untouched. Some of the developing countries are still at the growth stage of modern reforms such as Fintech, mobile money, etc.

According to UBS, almost 1 billion people in these emerging economies don’t have a formal bank account, neither access to financial services.
Here, we have a huge market for financial inclusion, services, and businesses. In the Sub-Saharan African region, there is a high volume of unbanked population. Over 90% of the financial transactions are done cash-based.
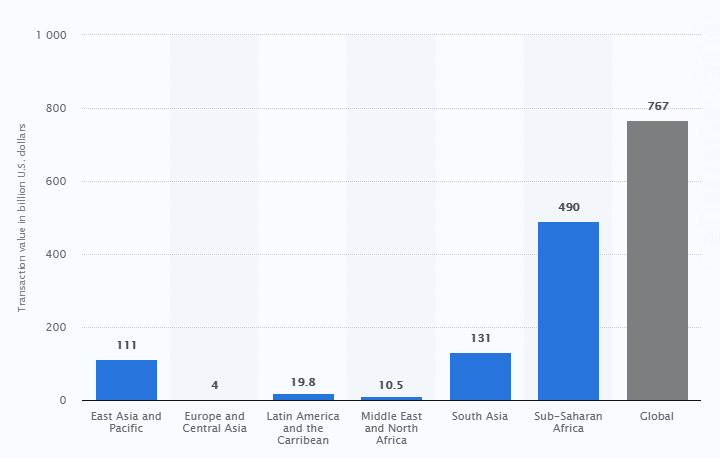
Currently, super apps like OPay and Jumia Pay rule these markets in financial as well as mobile money solutions but these and many other services such as Airtel Money, MTN, etc took years of effort to get over the challenges and issues that have led them where they are today. As of 2020, mobile money transactions have reached 490 billion dollars in the SSA region itself.
Some of the major challenges they faced while entering into the fintech market in SSA were:
Licensing and regulations – Bank-led model vs Central Bank regulation
Regulatory frameworks enacted were causing a hindrance in the establishment of fintech firms and businesses which are there to develop and increase the fast-paced development of the growing economy. Not keeping up with the reforms was a major reason behind the Fintech industry taking up a decade to become mainstream in the African Continent
Low levels of literacy – Rural population and illiteracy
Financial literacy is an essential tool to survive. Citizens need to be educated in terms of banking services, taxation, financial laws, and investments. Financial literacy helps one to budget, manage your loans and debt, save money and create long-term plans.
It allows youth to achieve their financial goals. Sub-Saharan Africans were not very educated or even literate when it comes to financing. This caused a problem for Fintech services as there was no understanding of finance or banking among the citizens.

Political interference
The biggest external threat to any industry would be the political threat. Banks in Africa are too reliant on government aid and it can cause hindrance in the rise of the Fintech industry as there can be political interference regarding laws and regulations.
This made it very difficult for the emerging businesses and the upcoming financial services looking to expand on the SSA region.
Heavy taxation – Continuous imposing of new taxes
African countries such as Uganda, Kenya, and the recently joined Zimbabwe are imposing heavy taxes on the Fintech industry. Even countries like Tanzania, Zambia, Benin, and Rwanda turned to the same solution for fixing a downfall in their fiscal deficits by increasing and imposing heavy taxes on mobile money services.
IT Security – Not a tech-savvy workforce
Africa being a developing country has regions where there is a shortage of basic human necessities as simple as food. People living in poverty and earning just enough to survive have no time to develop technological skills or social advancements. Thus, resulting in a workforce there which is not tech-savvy at all.
Since the inception of this concept in 2007, the Fintech industry has grown tremendously. Back then, the technology was not scalable making it difficult to keep up the cost and profitability.
Today, there are about 22 million smartphone users in the SSA region with majors services like MPesa, OPay, Jumia One, Airtel Money, MTN, etc providing financial inclusion and banking services to the unbanked population.
Even digitally, people can avail the benefits of e-wallets, banking services like withdrawals, deposits and loans, payment of bills and investments. Because the reforms are in the growth stage, there is constantly room for expansion and the rate of consumer adoption is also high.
For an instance, Uganda has seen a rise in financial inclusion because of Mobile Money. This is one of the many examples which has benefitted the population there and created scope for Fintech solutions.
Many of the benefits and impact seen due to this transformation are:
Improvement of financial literacy
According to S&P Global’s Financial Literacy Survey, African countries score worst in terms of financial literacy worldwide. Due to an increase in mobile money, there is an increase in terms of awareness, an increase in the number of users of banking services, and more educated customers for all financial institutions.
Elimination of financial exclusion
Financial inclusion has recently been one of the key concerns for developing countries. The Central Bank of West African States has made financial inclusion one of its top priorities by adopting new strategies.
Mobile money and the Fintech industry emerged as a solution for reducing the financial exclusion in these countries.
Secure storage for cash
Over 90% of the transactions in the African continent were cash-based. No security and no increase in the money. According to experts, money decreases when kept in cash whereas money increases if they are held in financial institutions.
Mobile money solutions have now changed the entire landscape of transactions as exchange of cash has decreased and more and more deposits are being made for using the online mode.
Easy and faster banking services for the customers
Mobile banking, mobile money, and digitization has created convenience and ease for the customers as there are options for fast, cashless payments, money transfers, and financial services. Even P2P Payment are now possible because of the Mobile Money concept.
Transaction-based revenue
Transaction based payment model is where the revenue is generated by directly selling an item or a service to the customer. It is also known as the “marketplace model” where the users engage in transactions and revenue is generated by charging these users a fee on each successful transaction.
Over 500 million subscribers were expected in the year 2020 and with the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, there is more need than ever to revolutionize digital financial services. Even when the growth is uneven, the SSA region showed a 12% increase in 2019 making it the leading continent for mobile-money services.
Mobile money in SSA will ensure an effective monetary policy by transforming cash-based transactions, adding currency and assets to the system, and creating a flow of money in the financial market.
Despite being new, this concept has had a positive impact on the financial health of banks and institutions. There is a significant increase in the adoption of banking services, enabling growth in the sector. Where there is a high level of adoption of mobile money, commercial banks have expanded and had more room for diversification.
While there is development in this sector, Covid-19 also played a major role in increasing the userbase for financial services. Using digital financial services was the only choice left during times of lockdown and pandemic.
Read More: Impact of COVID-19 on the payment industry
Due to that, many of these huge Fintech companies gained momentum with an ever-expanding business, more customers/users, and an increasing demand for mobile money services.
Today it is common in the Sub-Saharan African region for more citizens to have access to mobile money than having a traditional bank account. Covid-19 has served as a huge catalyst for the increasing adoption of Fintech and Mobile Money services in these countries.
Right now the market is ruled by major players such as:
MPesa
MPesa was the first-ever mobile money app to ever be launched in Africa. They used digital innovations, in the beginning, to develop the company and create value propositions. In its first month of operations itself, it acquired 20,000 customers which was way more than its target. Today, MPesa is used by over 48 million active users in the continent of Africa.
OPay
Opay (china-based) is an Africa-focused Fintech firm with a mobile money app. So far, the company has raised $170 million and has been emerging as the fastest-growing Fintech firm in the SSA region.
They started by launching their app in 2018 in Lagos and have expanded aggressively with ORide, an e-hailing service also as a part of it. OPay claims to be processing 80% of the bank transactions in Africa and 20% of the country’s non-merchant POS transactions.
The company has also acquired an international money transfer license for its international remittance service. OPay is currently known as a Super App with banking, mobile money, shopping, payments, e-hailing, tickets and reservations, online food ordering all services in one app.
Jumia Pay
Jumia Pay is, Africa’s very own super app launched by the e-commerce giant Jumia One in early 2018 ahead of OPay’s launch. It is also in competition with OPay as both of these businesses are expanding rapidly across the continent as Super Apps.
JumiaPAY also has similar services as OPay, with features of shopping, mobile money, finance and banking, e-hailing, reservations, ticket booking, online food ordering, etc.
Some of the features of Mobile Money that the users get are:
Strong KYC Implementation
Mobile money apps require KYC which is Know Your Customer. This means when new customers are onboarded, they must provide identity details and register with necessary documents. This is for assessing the customer’s risk of engaging in fraudulent or illicit financial transactions.
NFC Integration
NFC Integration solution is a highly secured communication protocol that facilitates contactless payments between NFC-enabled smartphones and merchant’s POS devices. It is a method of wireless data transfer that allows smartphones, tablets, laptops, to share data wirelessly via mobile wallets.
Peer to Peer payments
This feature allows users to transfer money from one wallet to another wirelessly. It allows peer-to-peer payment anytime, anywhere, making it easier for the user to transfer money at their convenience. It is a good feature for going cashless.
Payment from Bank to Bank
Mobile money transfer includes the bank to bank transfer feature also. It means you can send money from one bank to another in an instant, from the app itself. It is very convenient for the user as they don’t have to go to the bank physically to transfer the money manually and it saves time.
Merchant Payments
Many apps provide merchant payment solutions specifically for merchants’ convenience. All of their bulk payments, disbursements are made easy using these apps.
All of these apps are supported by API thus making it easier for merchants to get payments from customers through this app. Here, the customer initiates the purchase of the goods from their device after which the merchants get paid.
QR Payment
Apps now provide payments, money transfers through the QR code payment mode. The merchants have their own generated QR code and the customers can scan it. Just like that, every individual account gets a QR code that can be used to scan by a second party.
In the purchase option, the customer just has to scan the QR code, write the amount of money, and pay either from their application wallet or directly from the bank.
Bill Payments
Mobile money allows users to pay bills such as electricity, water, and it also allows users to pay rent, book tickets for shows, book tickets for transport, book hotel rooms, for shopping, for booking rides in taxis, and for recharges.
Any bookings and bill payments are now possible using mobile money where you can pay directly from the bank or you can pay using the funds in the mobile wallet.
Security
Mobile money gives you a foolproof platform for digital transactions and gives more security compared to cash-based transactions. Financial services require security and safety. Online, contactless transfers give you that privilege.
Mobile wallets are secured using technologies such as biometrics, passwords, pins, OTP authentication, tokenization, etc. Apart from that, they come with PCI DSS compliance which eliminates the chances of storing sensitive data. There is also GDPR compliance regulation and DSP2.
Rewards, coupons, discounts, points
Many of these money transfer apps have loyalty and reward programs, discount codes, promos, and points systems.
The more you use the app for your transactions, the more rewards you get, sometimes even discount codes for certain services such as restaurants or movie tickets or shopping for clothes. Customers love this feature the most as they love getting great deals on rewards, points, and discounts.
Loans and banking services
Mobile money provides the feature of loans as well as banking. The customers get all the banking services from loans, deposits, insurance, withdrawals, etc. Instant registration and process of creating bank accounts and integration of customer data is done in case of new bank accounts or in case of loans.
Users can budget and plan
Users also get the options of analyzing their transactions, their spending and creating budgets, and planning their finances. A budget allows you to set a limit to your expenses, organizing your transactions and spend and income, sending reminders, organizing your bills and your savings.
Conclusion
Mobile money is the future of finance and banking. In the Sub-Saharan African region, Mobile money is already gaining momentum and it has a scope of development further as there is a high adoption rate for using mobile money services rather than going with cash.
Also, due to Covid, people are now preferring the cashless system which in the long run will help Fintech firms develop and establish their solutions in this market.