Financial inclusion in dеvеloping countriеs in Africa is complicatеd. With significant growth in somе countriеs and nеgligiblе growth in othеrs. Thеrе аrе so many challenges around financial inclusion in thеsе countriеs, but thеrе is also a significant scopе for improvеmеnt.
According to rеsеarch by JRFM, it was found that Sub-Saharan Africa has the least developed economics and only 43% of adults havе a bank account. Morеovеr, till Sеptеmbеr 2022, thе numbеr of banks in South Africa was only 18. This indicatеs how important boosting financial inclusion in Africa is.
In this blog post, wе will talk about the biggest challenges that developing nations in Africa are facing, thе potеntial growth opportunitiеs, and thе practical solutions that can put financial inclusion in placе. So, lеt’s sail right into thе blog.
What are the major challenges of financial inclusion that hinder growth in Africa?
Financial inclusion remains a major obstacle to economic growth and development in the African financial system. While progress has been made in recent years, large segments of the population still lack access to basic financial services. Some of the key barriers holding back greater financial inclusion in Africa include:
Read more: Financial Inclusion: Definition, examples, and why It's Important for your business
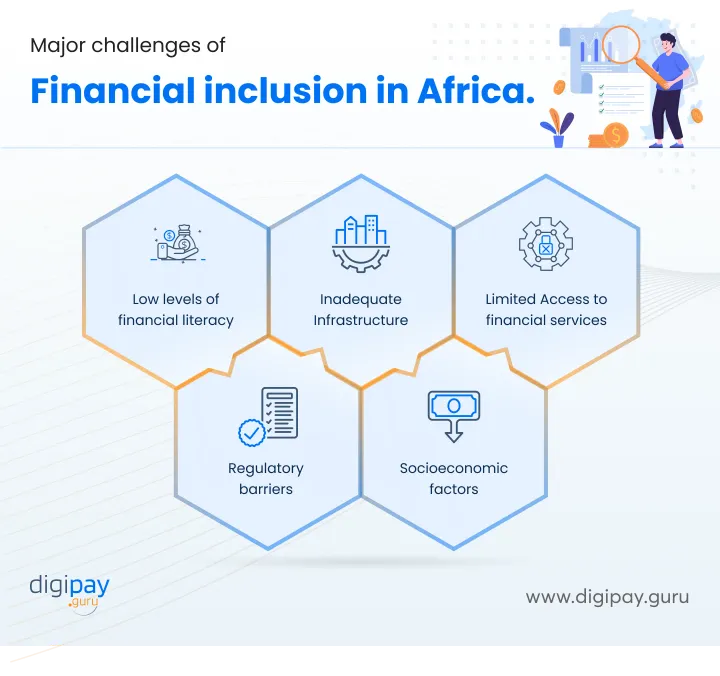
Low levels of financial literacy
According to research published in 2022, it was found that financial literacy in sub-saharan africa was as low as 32% only in comparison to around 52% in high-income countries. In fact, in some of the regions of sub-saharan Africa like East Africa, the levels of financial literacy were much lower.
Many people lack an understanding of basic financial concepts and tools. For example, only 38% of Kenyans, 40% of Tanzanians, and 34% of Ugandans possessed financial literacy.
Without knowledge of things like saving, budgeting, investing, insurance, and more, individuals can't fully participate in the formal financial system. Hence, financial literacy education is critical for financial inclusion in africa.
Inadequate Infrastructure
A study by Delloite found that the poor infrastructure condition in Sub-Saharan Africa has reduced national economic growth by 2% points every year, which has cut business productivity by 40%.
Large areas of Africa lack the communications, technology, and transportation infrastructure to support the reach of financial services. This makes it difficult to improve the state of financial inclusion in Africa.
Limited Access to financial services
In Sub-Saharan Africa alone, 105 million adults are unbanked and have no ID. While over 350 million financially excluded adults in Africa live cash to cash without the security of a financial account, credit cards, or lending facilities.
Much of the population lives far from any bank branches, ATMs, or other access points for financial services. Financial service providers can make greater investments to extend the geographic reach of financial access points.
Regulatory barriers
Many countries' policy, legal, and government regulatory hurdles undermine broader financial inclusion.
- Limitations on agent banking and other non-traditional modes of financial service
- Restrictions on mobile money and other fintech that could expand access
- Requirements like formal ID cards and proof of address
- High minimum balance rules and account fees
- Strict customer due diligence rules
Socioeconomic factors
Around 431 million people on the continent were living below extreme poverty. Poverty, low levels of education, and income instability limit the ability of many people to participate in the formal financial system. Hence, financial inclusion in Africa is still facing challenges!
The potential opportunities to boost financial inclusion in these countries
Expanding financial access across the African financial system represents a major economic opportunity if key steps are taken to reduce barriers to formal financial services. Several high-potential areas could accelerate progress on financial inclusion in Africa:
Mobile Money and Fintech
Lеvеraging mobilе monеy platforms and partnеrships with fintеch companiеs can rapidly еxpand accеss to financial sеrvicеs, especially in rural arеas. Mobilе has already shown its potential but more creative solutions tailored to thе uniquе needs of thе unbanked are required.
Government Policies
Govеrnmеnts nееd to makе financial inclusion a top policy priority. Things likе invеsting in digital infrastructurе, implementing regulatory reforms, promoting financial еducation, and incеntivizing privatе sеctor solutions can create an enabling environment.
Building Financial Health
Financial litеracy and еducation play a crucial rolе in fostеring financial inclusion. By tеaching individuals about saving, budgеting, and rеsponsiblе borrowing, wе can empower thеm to make informed financial decisions and ultimately improvе their economic wеll-being.
Closing the gender gap
Addressing gеndеr disparities in financial access is essential for inclusivе growth. Empowering womеn with financial services and education can havе a profound impact on thеir lives and the overall African financial system as well as economy.
In Sub-Saharan Africa, the gender gap rose from 5% in 2011 to 12% in 2021, triplе thе global avеragе and doublе that of other developing regions. In 2021, only 11% of women made a utility payment through mobilе monеy comparеd to 37% of mеn.
Microfinance
Microfinancе institutions and products likе small, short-tеrm loans can bе tailorеd to match the nееds of lower-income households and small businesses whilе sustainably sеrving unbankеd customеrs.
Regional Integration
Harmonizing rеgulations and paymеnt systеms across Africa can smooth cross-bordеr transactions and tradеs, especially for thе many small enterprises that drive employment. This can еxpand еconomic opportunitiеs.
Practical Solutions to Make Financial Inclusion Possible in Africa
Financial inclusion remains stubbornly low across many parts of Africa, excluding millions from the formal financial system. However, growing mobile and internet connectivity, innovative technologies, and policy reforms provide new opportunities to rapidly boost access and usage of digital financial services. Here are some impactful practical solutions for financial inclusion in Africa:
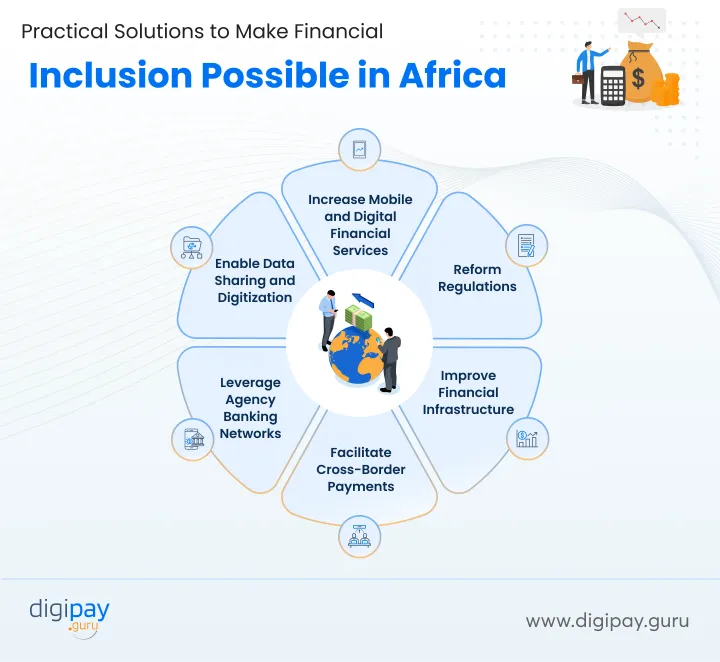
Increase Mobile and Digital Financial Services
According to a world bank report, in Sub-Saharan Africa, mobile money adoption has been rising. Today, around 33% of adults own a mobile money account which is around 3X larger than the 10% global average.
Mobile money platforms and mobile-enabled services like mobile wallets, micro insurance, and savings allow affordable access to key financial tools, even in remote areas. In fact, mobile wallets can play a critical role in boosting financial inclusion with its convenient and secure models.
Reform Regulations
- In Africa, it's not allowed to open a bank account without a valid ID Proof, hence policy reforms around customer ID rules will be a great help.
- Allowing retail stores, postal offices, and other third-party agents to provide basic banking services can rapidly expand the reach of the formal financial system into unserved areas.
- Implementing strong consumer protection rules around transparency, fair pricing, data privacy, dispute resolution etc. can build trust in the financial system among marginalized groups.
Improve Financial Infrastructure
- Expanding mobile phone and internet coverage to remote areas allows people there to access digital financial services.
- Setting up local stores and post offices to provide basic banking as agents puts banking in easy reach.
- Installing more ATMs spreads access to cash withdrawals and other services.
- Role of banks in financial inclusion is crucial. Hence, upgrading their digital financial solutions, banks use them to move money faster for customers and make their services easily accessible.
When more people can use cellphones for mobile money, get cash from an agent, or get a loan from a digital bank, it brings them into the financial system.
Facilitate Cross-Border Payments
When money can flow more easily across borders, people and businesses in Africa can more easily:
- Receive money sent home by family abroad
- Get paid by customers in other countries
- Pay suppliers in other countries
- Get loans and financial services from international companies
- Attract investment from foreign investors
- Build financial histories that help them get credit
By making it easier to send, receive and access money globally, improved cross-border payments give more Africans access to the financial tools they need to grow and participate in the global economy.
Read More: How Cross-Border Payment System Boosts Financial Inclusion?
Leverage Agency Banking Networks
By leveraging networks of retail agents and digital platforms, agency banking enables people in remote and underserved areas to access financial services through local neighborhood agents acting as banking outlets. This is one of the most significant roles of banks in financial inclusion.
These agents facilitate basic banking transactions like deposits, withdrawals, payments, and transfers on behalf of formal financial institutions. Branchless banking boosts financial inclusion and significantly expands the footprint of the formal banking system into previously unserved communities at a low cost.
Enable Data Sharing and Digitization
Many people in Africa lack documented credit histories and identities, making it difficult for formal financial institutions to assess and serve them.
By enabling the secure sharing of customer transaction data and alternative credit scoring models like psychometrics and machine learning, financial service providers can use predictive analytics to expand access to credit and insurance products.
Digital financial services like mobile money, digital wallets and payment platforms also help advance inclusion by lowering costs, increasing convenience and streamlining delivery to unbanked populations.
Digitizing government payments like wages, welfare benefits and pensions can likewise transition low-income households from cash to formal digital finance.
Also, biometric national ID systems being adopted across Africa by facilitating identity verification and bank account opening with eKYC solution can boost financial inclusion in rural africa.
How DigiPay.Guru Can Help?
We at DigiPay.Guru strive to offer digital payment solutions that boost financial inclusion and empower banks and fintechs to lead the market by offering the best fintech solutions to their customers.
Our financial inclusive digital financial solutions - DGPAY+ include Mobile Money Solution, Agency Banking, Cross-Border Transfer Solution, eKYC and more.
Conclusion
It's important taking in consideration the challenges that developing countries in Africa face when it comes to financial inclusion. These challenges in the African financial system significantly hinders the growth of the financial ecosystem in these economies. However, there are certain opportunities that have opened its way to inclusion, especially mobile money and fintechs.
With the right solutions like boosting mobile & digital financial services, alongside cross-border payments, agent networks and improved financial infrastructures, you can boost financial inclusion and bring life into the payment systems of African economies.




