The number of global digital payment users is projected to reach 8.34 billion by 2030!
Plus, the digital finance world is bursting with innovation. With this, mobile wallets and mobile banking have become popular payment systems among your customers.
Both mobile wallets and mobile banking enable users to make payments, manage funds, and access their financial data on their handheld devices. This makes them more convenient and seamless than ever before.
Nonetheless, despite their likenesses, mobile wallets and mobile banking are two separate technologies with diverse features, functionality, and use cases.
In this guide, you will learn deeply about mobile wallets and mobile banking to help you comprehend the differences between these two technologies to make informed decisions.
You will also get a clear and concise overview of what mobile wallets and mobile banking are, how they work, their features, and mobile wallet vs mobile banking to understand what makes them different from one another.
So, lets get started and explore the world of mobile payments together!
What Are Mobile Wallets?
Mobile wallets, also known as eWallets or mobile payment apps, are electronic versions of traditional wallets that allow users to store funds and use their credit and debit cards, loyalty cards, coupons, and other types of payment information on their mobile devices.
According to the latest study by the Business Research Company, the global market for mobile wallets is expected to reach around $8,404.8 billion by 2029. This figure shows a significant increase and constant popularity of mobile wallets.
Mobile wallets are a game-changer, especially in regions with limited bank branch access. From peer-to-peer payments to merchant QR scans, they are fast, frictionless, and built for the future.
Some popular examples of mobile wallet apps include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.

How Mobile Wallets Work
Unlike mobile banking, which connects directly to a bank account, a mobile wallet stores a prepaid balance or links to cards and accounts. Here’s how it works:
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
|---|---|---|
| User downloads a mobile wallet app and sets up an account | User links their credit/debit card information to the mobile wallet | User selects the card they want to use for the transaction |
| Step 4 | Step 5 | Step 6 |
| User holds their mobile device near the contactless payment terminal | The terminal uses NFC technology to communicate with the mobile wallet | Payment is processed automatically |
Key Mobile Wallet Features
Mobile wallets today go far beyond just storing digital cash. They’re powerful, feature-rich platforms designed to handle everyday payments, business use cases, and financial inclusion goals—all from a mobile device.
Here’s what a modern wallet banking solution brings to the table:
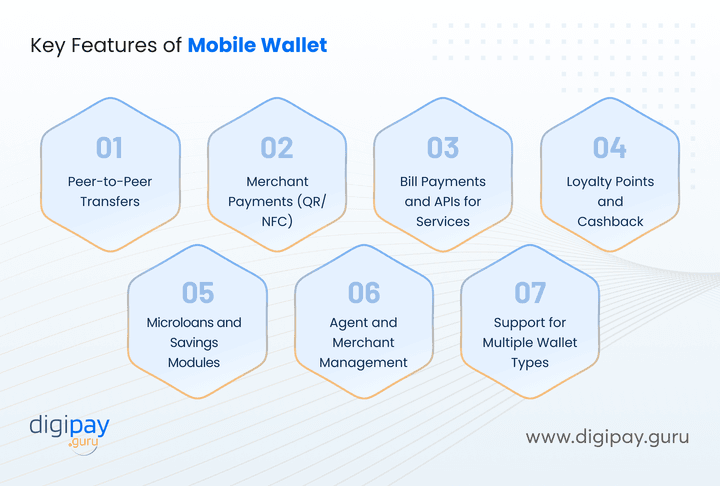
Peer-to-Peer Transfers: Users can instantly send money to friends, family, or vendors with just a phone number or wallet ID. It’s fast, simple, and perfect for daily micro-transactions or splitting bills on the go.
Merchant Payments (QR/NFC): Merchants can accept payments using QR codes or NFC taps, eliminating the need for POS machines. It lowers hardware costs and expands digital acceptance to even the smallest businesses.
Bill Payments and APIs for Services: From electricity bills to mobile top-ups, wallets can integrate with utility providers via APIs. This creates recurring engagement and lets users manage essential services in one app.
Loyalty Points and Cashback: Integrated reward engines allow users to earn and redeem points or receive cashback after transactions. It encourages repeat usage and builds brand loyalty, especially in competitive markets.
Microloans and Savings Modules: Offer short-term credit or enable goal-based savings directly in the wallet. Perfect for unbanked users or gig workers with irregular income. This helps them access basic financial services.
Agent and Merchant Management: Enable a decentralized distribution model through agents and merchant partners. These modules help grow your network quickly, even in areas without internet or banking infrastructure.
Support for Multiple Wallet Types: Launch closed-loop, semi-closed, or open-loop wallets depending on your market and regulatory model. This flexibility allows you to serve everything from campuses to national economies.
Pros of Mobile Wallets
Convenience: Mobile wallets eliminate the need to carry multiple physical cards, which makes them easier to manage finances on the go.
Security: Mobile wallet solutions use advanced security features such as tokenization, MFA, biometrics, and encryption to protect users funds along with personal and financial information. This ensures a secure online payment system for the customers.
Read more: Protect your customers with a secure online payment system
Speed: Mobile wallets allow for fast and easy payments, which eliminates the need to physically hand over credit or debit cards.
Rewards and Discounts: Some mobile wallets offer rewards and discounts for using the app to make payments. And some come up with loyalty and reward programs. These rewards and discounts help you retain customers and keep them happy.
Digital Record: Transactions made through mobile wallets are saved digitally, which makes it easy for the user to keep track of their expenses.
Multi-Currency Support: Some mobile wallets allow users to store and use multiple currency cards, which makes it convenient for international travelers and customers who have to transact across borders.
Increased Merchant Acceptance: Many merchants now accept mobile wallet payments, which makes it a widely accepted form of payment. This increases profits and customer base, all at once.
Contactless Payments: Mobile wallets enable contactless payments, which reduce the risk of transmitting germs and the spread of disease. Plus, its extra convenient and fast, which is exactly what modern customers want.
Cons of Mobile Wallets
Vulnerability to Hacking: Mobile wallets can be vulnerable to hacking and other types of cybercrime. So users should be cautious and keep their mobile devices secure at all times.
Additional Fees: Some mobile wallets may charge additional fees for certain services, and these fees are even hidden. This calls for a lack of trust among customers.
Limited to Specific Countries: Some mobile wallets are only available in specific countries, which makes them unavailable for international users.
Data Privacy Concerns: Storing personal and financial information on mobile devices can raise data privacy concerns if the mobile wallets are not protected with strong security measures and tools.
What is Mobile Banking?
Mobile banking refers to the ability to access and manage your bank account(s) and financial information digitally through a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet.
This includes a wide range of services such as checking account balances, transferring money, paying bills, depositing checks, managing account settings, and more.
How Mobile Banking Works
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
|---|---|---|
| User downloads a mobile banking app or accesses a mobile-optimized website provided by their bank or financial institution | User enters their login credentials to access their account information | User can now access and manage their account information and perform transactions such as checking account balances, transferring money, paying bills, depositing checks, and managing account settings |
Major Features of Mobile Banking
Mobile banking apps are built to mirror the full-service experience of visiting a branch. But with the convenience of doing it all from your phone.
Here’s what most modern mobile banking solutions deliver to your users:
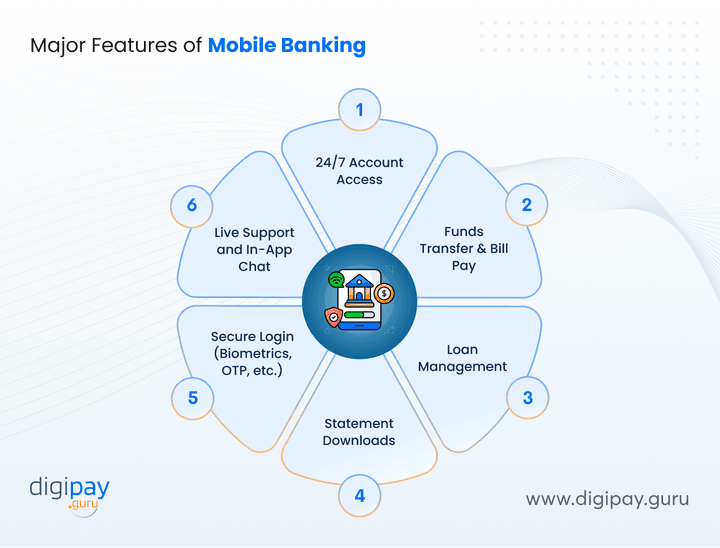
24/7 Account Access: Users can check balances, track transactions, and view account history anytime. No need to wait in lines or visit branches—everything’s available on demand.
Funds Transfer & Bill Pay: Users can transfer funds between accounts, send money to others, and pay utility bills. This seamless functionality helps banks stay relevant in the digital-first world.
Loan Management: From applying for personal loans to tracking EMIs, mobile banking apps allow full control over credit. Some also offer pre-approved loan offers based on credit behavior.
Statement Downloads: Customers can easily generate and download their bank statements for tax filing, proof of funds, or business use—without needing to request them manually.
Secure Login (Biometrics, OTP, etc.): Top-tier security features like multi-factor authentication, OTPs, and biometric authentication (face/fingerprint) are built-in to protect sensitive financial data.
Live Support and In-App Chat: Real-time assistance through chatbots or live agents helps improve customer trust. Many banks integrate AI-powered chat to handle basic queries instantly.
Pros of Mobile Banking
Accessibility: Mobile banking allows users to access their account information and perform transactions anytime, anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection.
Convenience: With mobile banking, users can perform transactions such as checking account balances, transferring money, paying bills, depositing checks, and managing account settings without visiting a physical bank branch or ATM. This makes it very convenient for users
Security: Mobile banking utilizes advanced security features like biometric technology in digital payment (for authentication), tokenization, encryption, and multi-factor verification to protect users personal and financial information. Plus, it helps avoid any unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
Real-time Updates: Users can get real-time updates on their account transactions, balances, and other information. This way, they will stay more engaged and informed with your platform.
Digital Record: Transactions made through mobile banking are saved digitally, which makes it easy for the user to keep track of their expenses. This also helps you to understand their patterns and improve your offerings accordingly.
Easy Account Management: Mobile banking allows users to easily manage their account settings and preferences.
Widely Available: Most banks and financial institutions offer mobile banking services, which makes it a widely available digital banking service all across the globe. Lower Costs: Mobile banking can reduce the cost of traditional banking services such as check depositing, money transfer, and account management. This is because its done all through one app with no extra intermediaries or hidden fees.
Contactless Payments: Mobile banking enables contactless payments, which reduce the risk of transmitting germs and the spread of disease. This came to light and was implemented full-fledged during the time of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read more: How contactless payments drove digital payments during Covid-19
Better Budgeting and Tracking: Some mobile banking software or apps offer budgeting tools and the ability to view account transaction history, which can help users better track and manage their expenses.
Cons of Mobile Banking
Security Concerns: Mobile banking is vulnerable to hacking and other types of cybercrime, so users should be cautious and keep their mobile devices secure at all times.
Technical Issues: Mobile banking may be prone to technical issues such as system downtime or app crashes, which can cause inconvenience to users.
Limited Services: Some banks and financial institutions may not offer all the services that a user may need through mobile banking. There can be a digital limitation if the solution you opted for to make the app is not robust enough.
Data Privacy Concerns: Storing personal and financial information on mobile devices can raise data privacy concerns.
Difference Between Mobile Wallets And Mobile Banking
| Aspect | Mobile Wallet | Mobile Banking |
|---|---|---|
| What is it | Storing and using payment information (credit/debit cards, loyalty cards, coupons) | Accessing and managing bank account(s) and financial information |
| Security | Use of advanced security features such as tokenization and encryption | Use of advanced security features such as biometric authentication, encryption, and multi-factor authentication |
| How it Works | Quick and easy way to make payments | Comprehensive account management and various services such as checking account balances, transferring money, paying bills, depositing checks and managing account settings |
| Acceptance | Accepted by a growing number of merchants | Generally accepted by all banks and financial institutions |
| Go-to-Market Speed | Quick launch with fewer compliance and integration layers | Slower launch due to regulatory and infrastructure requirements |
| Primary Use Cases | P2P transfers, bill payments, QR payments, merchant and agent-based payments | Checking balances, transferring funds, managing loans and deposits |
| Infrastructure Dependency | Can operate independently from core banking systems | Tied closely to core banking infrastructure |
| Offline Accessibility | Supports USSD, QR, agent-assisted models for low-connectivity environments | Requires stable internet connectivity for real-time banking features |
| Revenue Opportunities | Enables monetization through merchant fees, transaction fees, and value-added services | Cross-sell loans, insurance, credit cards, and investment products |
| Best Fit For | Fintechs, telcos, digital-first banks, and financial inclusion programs | Traditional banks, neobanks, and regulated financial institutions |
All in all, both mobile wallets and mobile banking play a crucial role in the digital payments landscape.
If youre looking for a convenient and secure way to make payments, a mobile wallet may be the perfect solution. However, if you are looking for more comprehensive account management, mobile banking could be the way to go.
To understand this better, lets look at the next section, which talks about when to choose what.
When to Choose What: A Strategic Lens for Banks and Fintechs
Now let’s get real. You’re not choosing based on what’s cooler. You’re choosing based on what grows your business.
When Mobile Banking Makes Sense
-
You already have a full-fledged banking system
-
Your customer base is entirely banked and digitally active
-
You want to enhance customer experience, not acquire new unbanked customers
-
You need full access to financial services like loans and deposits in-app
When Mobile Wallet (eWallet) is the Smarter Choice
-
You want to tap into the unbanked or underbanked
-
You’re entering emerging markets with low banking penetration
-
You need fast GTM (go-to-market) with low cost
-
You’re building an agent-based model
-
Youre a fintech, telco, or neobank looking to diversify services
-
You want to roll out wallet banking apps with scalable APIs and rich payment flows
TL;DR: If you’re looking for reach, growth, and flexibility, start with a mobile wallet. You can always evolve into full banking later.
How DigiPay.Guru Helps You Launch Your Own Mobile Wallet
At DigiPay.Guru, we specialize in helping banks, fintechs, and telcos unlock growth with powerful, customizable mobile money solutions.
Our solution isn’t just another eWallet. It’s a modular, scalable, and compliant solution built to help you:
-
Go live fast with prebuilt modules
-
Reach underserved segments through agent and merchant networks
-
Scale across markets with interoperability and flexible architecture
Key Capabilities That Set Us Apart
-
Multi-wallet support (closed, open, semi-closed)
-
Agent & merchant module for network expansion
-
Bill payments & third-party API integrations
-
Compliance-ready engine (KYC, AML, PCI-DSS)
-
Wallet banking app with rich UI/UX
-
Offline capabilities for low-connectivity zones
-
Analytics & reporting dashboards
Plus,
We also offer mobile banking software if your roadmap includes full-service banking later.
And no, we won’t sell you what you don’t need. We help you launch what fits your business, not what sounds good in pitch decks.
Conclusion
Both mobile wallets and mobile banking offer convenient and secure ways to manage one s finances, but they have distinct features and functionality. Mobile wallets focus primarily on the storage and use of payment information, while mobile banking allows users to access and manage their bank account(s) and financial information.
So, its clear that the choice between a mobile wallet and mobile banking will depend on your individual needs and preferences. For a convenient and secure way to make payments, a mobile wallet may be the perfect solution. However, for more comprehensive account management, mobile banking could be the way to go.
We at DigiPay.Guru, offer both advanced mobile money solutions, i.e., mobile wallets, and mobile banking to cater to your diverse needs. Our eWallet solution is designed to be secure, easy to use, and accepted by a wide range of merchants.
Whereas, our mobile banking solution is designed to provide you with comprehensive account management and various services to offer, such as checking account balances, transferring money, paying bills, depositing checks, managing account settings, and more.

FAQ’s
A bank is a licensed financial institution that offers a full suite of services, like savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and more. A wallet, on the other hand, is a digital tool (usually mobile-based) used for making payments, storing money, and accessing lightweight financial services without the need for a full-fledged bank account.
In simple terms: A bank holds your money and gives you structured financial products. A wallet lets you spend, transfer, and manage money instantly—often with lower entry barriers.
Absolutely. Some of the most recognized mobile wallet apps around the world include:
-
Paytm (India)
-
M-Pesa (Kenya, Tanzania)
-
Gcash (Philippines)
-
Venmo (USA)
-
Alipay (China)
-
Orange Money (Africa)
Each of these platforms enables peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, contactless payments, and more. This makes them powerful tools for financial inclusion and digital commerce.
Not quite. While they both live on mobile devices and offer digital convenience, they serve different financial needs.
-
Mobile banking is an extension of a traditional bank account—used for managing funds, applying for loans, or checking balances.
-
A mobile wallet is often prepaid and built for fast payments, transfers, and microservices. You may not need a bank account to use one.
Think of mobile banking as managing your entire financial portfolio, while a mobile wallet is built for daily spending and simplified transactions.
A wallet is typically a digital storage for money that is preloaded via bank transfer, cash-in agents, or cards. It’s great for fast transactions, bill pay, and everyday financial interactions.
A bank account, however, is a formal relationship with a regulated financial institution. It provides access to interest-earning deposits, credit lines, loan products, and regulatory protections.
While a bank account offers depth, a wallet offers speed and accessibility, especially in markets with low banking penetration.



