Agency banking was introduced for the first time in 2013 in Bangladesh, with the aim to provide banking services to economically backward and underserved populations, especially those who live in rural locations and very far from banks.

Research by the World bank states that according to a Global Findex report 2021 (released in 2022), the global population of approx. 1.4 billion people are still unbanked. This (1.4 billion) is not at all a small number. And as history says, agency banking’s primary aim is to help the unbanked and underserved populations. That’s the reason why the adoption of agency banking was considered by the banks.
In this blog, we will discuss what agency banking is, why it is needed, who banking agents are, how it works, the major parties, its advantages, the services, and the use cases of its successful implementation.
What is the meaning of agency banking?
Victor was a farmer in a village very far from the city, and his son had started his high school study at a boarding school in the city. One day his son got sick and had an urgent need for some extra cash. Victor wanted to send him the money immediately, but there was no bank in the village.
Victor did not have extra cash other than the amount he wanted to transfer to his son. So, he felt disappointed and helpless. But then his friend told him that his bank had introduced an agency banking service in the village, available at the nearby grocery store. Victor visits there and successfully transfers money to his son.
Agency banking acted as a life-saver for Victor. So without further delay, let's understand what exactly is agency banking! In layman's terms, Agency banking is a service introduced by banks that allows them to offer their banking services without having traditional branches in areas that do not have easy access to financial services.
The need & importance of agency banking
Now that you know what agency banking is, aren't you curious to know what led to agency banking? Why did the need for agency banking rise?

Well, the key reason for this was the challenges faced by the traditional banking system.
High operation and setup cost
Setting up a traditional bank in every place is next to impossible. But anyhow, if the bank tries to do it, the costs to set up and operate are so high that it would be a loss-making initiative for them. Agency banking has taken away this burden from the banks, and now they are providing their services regardless of the physical location.
Limited scaling capabilities
Traditional banks were not able to extend their services to the areas where there were no banks. There was no way to do that until the people from that area could come to the bank. This made banks miss out on many customers leading to limited scalability opportunities.
With the impact of agent banking and its branchless functionalities, it became possible to extend banking services to a larger population leading to the increased ability to scale for banks
Low Profitability
When there were only brick-and-mortar banks (traditional banks), they could only cater to the customers that visited banks. Then when online banking started, they could cater to customers who were already associated with traditional banking and had their bank accounts, but in the online form. So, their profit was limited to these customers only.
Hence with the arrival of agency banking services, banking services are reaching every nook and corner, and with more customers, more profit is an obvious byproduct.
Lack of Agility
Traditional banks are less agile and flexible in terms of adapting to change and catering to customer needs and preferences. But the customers look forward to fast and more convenient services, which is a challenge for the traditional bank to keep up with.
On the contrary, by making several services available for agency banking, traditional banks can extend their services quickly and effectively to their customers, especially those who reside in remote and underserved areas.
Owing to these challenges in traditional banking, the importance of agency banking rose, and today it is accepted and utilized widely by almost all banks to extend their services.
In simple words, a “banking agent is a third party who provides banking services on behalf of a bank to customers.”
The banking agents provide these banking services in remote, unbanked, and underserved areas. Generally, the small shops, grocery stores, gas stations, or postal services in these areas become the banking agents with a bank to provide various banking services like cash deposits, withdrawals, balance inquiries, and many more.
The banking agents operate in different ways, such as some agents provide services by going door-to-door with their mobile phones, tablets, or m-POS machines. Some agents do the same, but from a fixed location in areas that are within easy reach of the customers.
Thus, banking agents are a vital part of the agency banking process. But how exactly does the agency banking process work?
How does agency banking work?
To provide agency banking services, the banks need to offer an advanced agency banking solution that facilitates a seamless banking experience for the customer and smoother coordination among all the components of agency banking mentioned above. Below are the steps as to how branchless (agency) banking works.
Bank and banking agent come into a contract
In the first stage, the retailer gets authorized as a banking agent by his respective bank or financial institution, and they sign a contract for extending the banking or financial services.
Create an m-wallet for agents
After the authorization and contract process is completed, the banking service provider creates mWallet for the banking agent. This wallet allows the agent to deposit and manage funds electronically. Once the mWallet is created, the banking agent deposits a prepaid balance in the wallet to begin providing services to customers.
The customer opens his bank account
Now, customers can open their bank account and avail of basic services like cash deposits and withdrawals by simply visiting the nearest banking agent with a valid ID.
Initiation of the transaction
If a customer wants to initiate a transaction, he can visit the agent and ask for the type of transaction he wants to make. The agent will then initiate the transaction in cash or card (as per customer preference).
Confirmation of transaction
Once the agent initiates the transaction through his system, the bank processes it and facilitates the transaction for the customer. And on successful processing, the agent confirms it by assigning a transaction receipt to the customer.
Parties involved in agency banking
Now that we know how agency banking works, let's take a clear understanding of the parties involved in the process of agency banking.
Agency banking service providers
Agency banking service providers are responsible for managing various banking agents. They are also responsible for operating services, marketing, cash handling, branding, and many more.
As discussed earlier, banking agents are the retailers authorized to perform various banking services on behalf of banks and financial institutions. They provide various banking services to customers.
Banks/Financial institutions
Banks and financial institutions are the hosts that comprise both consumer and agent accounts. These are entities through which the actual cash flow takes place.
Read More: What is Fintech and what is its impact on banking?
Super/sub-agents
Banking agents can also form other agents under them and get an additional commission for every transaction they make. This way, these banking agents will be called super/sub-agents.
Consumers
Consumers are the end-users of agency banking. These are generally those people who don’t have a bank account but have access to mobile phones or those who reside in remote and underserved areas where there are no brick-and-mortar banks.
Advantages of agency banking for banks
When the need for agency banking arose, the main benefit that was in mind was extending banking services to the population in the areas where the banks could not establish their branches. Some major benefits of agency banking for banks are:
Minimized Costs
Agency banking is a cost-effective way for banks and financial institutions to extend their services in areas having lower penetration of banks. Due to the agency banking model, banks and financial institutions don’t need to set up a physical branch which reduces operational, infrastructure, maintenance, and other high-capital investment costs.
Agency banking allows banks to kill two birds with one stone. First, they can save the cost required to set up a new branch because maintaining a traditional bank is around 25% costlier than managing the network of agents. Second, they can increase profitability by driving business from previously untapped areas.
Increase in customer base
Banking agents allow banks and financial institutions to expand their customer base by offering services to a larger number of unbanked and untapped customers. This increase in the number of customers can lead to a significant increase in profits for banks.
Similarly, with agency banking, the banks can have a large number of agents under them, which in turn, brings more customers to the bank and financial institutions.
Better maintenance of asset quality
Banking agents are often familiar with clients and their financial situations, including repayment capacity and stability. This know-how can help banks to make informed decisions when deciding whether to lend money. Hence the banks can easily maintain the quality of their assets and protect their financial health.
Build trust and awareness among the customers
The presence of banking agents in the formal banking system brings a human touch that users find comforting. They find comfort as they can interact with someone they know. This is precisely the reason why there has been an increased level of trust for agents rather than bank branches.
With such comfort and convenience, clients feel safe performing all the financial operations they need. Such trust in banking agents encourages their whole community (in a particular area) to utilize agency banking in their regions.
Enriched customer experience
Agency banking, also known as branchless banking, allows banks to bring their services directly to users rather than requiring them to visit a physical branch. This convenience has led to an enhanced customer experience, as clients can simply visit agents nearby rather than travel and wait at a bank branch.
Users can perform various banking operations through their agents, such as withdrawing/depositing funds, paying bills, loan payments, and many more, just with a formal ID or biometric.
Agency banking is an easy platform for users as it delivers various banking solutions for the unbanked population using phones, card readers, POS (point-of-sale) terminals, and many other cutting-edge technologies for processing real-time transactions.
High security
In addition to convenience, agency banking offers top-notch security. Customers can obtain a magnetic chip card or stripe, and a bank pin, which they can use at the agent's terminal to carry out transactions. These methods of payment are more secure than using cash.
Read More: DigiPay: A foolproof platform for digital transactions
Services provided by banks via agency banking
Banks and financial institutions offer a wide range of services through agency banking. The agency banking services include
-
Cash deposits: The customers pay in cash to the agent, and the agent then transfers the amount to the customer’s account.
-
Cash withdrawals: The customer requests a particular amount of money to withdraw, and the agents provide customers with cash of the same amount.
-
Balance inquiries: The customer asks for the balance in his account, and the agent checks in his system and provides the balance details in written or spoken words.
-
Mini statements: The banking agent can generate a mini statement of a customer’s transaction history in a digital or physical copy through the banking system used by them.
-
Account transfers: The customers need to provide basic account information or the phone number of the person to whom they want to transfer funds. Agent bank will do it for them.
-
Customer loan applications: Customers can apply for loans with the help of agency banking. They can get the loan application filled in by the agents.
-
Utility bills: The customer can pay utility bills like electricity, water supply, gas supply, and many more.
-
Customer onboarding: The customers can open their bank accounts and onboard themselves to a particular bank of their choice.
-
Loan repayments: Customers can bring in cash and ask for loan repayments with the help of banking agents without having to pay monthly visits and incur heavy travel costs.
-
Credit card payments: If the customer has a credit card, he can get the payment done from the convenience of his proximity.
-
Registration for different services: When banks have various schemes or new beneficial services to offer, the customers can easily avail of these services by registering through an agency banking service.
Successful implementation of agency banking
One of the biggest hurdles banks faced was providing banking services in rural areas. Because to open a bank branch in a rural area, high OPEX/CAPEX (operational/capital expenditure) is needed.
However, there’s no certainty that the bank would get enough return on investment (ROI). This is one of the prominent reasons why banks fail to reach rural users. Also, rural users have not yet developed a habit of using mobile financial solutions.
But now, with agency banking, the banks have reached rural areas and provided banking services to a large section of the unbanked population throughout the world. Here we’ll discuss the use cases of the impact of agency banking in a few countries.
Kenya
A study by statista says that as of 2020, there were around 72,617 bank agents in Kenya alone. This stat makes it pretty clear, there has been a positive impact of agency banking in the country.
Talking about financial inclusion, the latest report by Deloitte, the usage of financial products (formal access to financial services) in Kenya increased to 83.7% in 2021, up from 66.7% in 2013. The report also states that today millions of previously underserved people of Kenya use formal financial services daily via their mobile phones
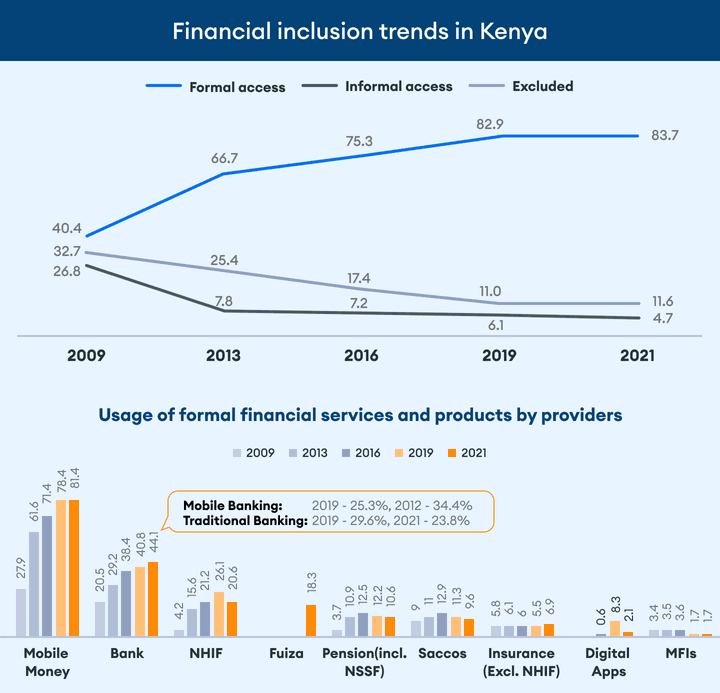
According to tracxn, there are nearly 403+ fintech startups in Kenya as of 2022. This figure is also one reason for the big number of agent banks in the country.
Read more: The future of agency banking in Kenya
Bangladesh
According to the latest study by Bangladesh bank (Central Bank of Bangladesh), nearly 7.6 million bank accounts were associated with agent banking in July 2020. This figure represents a year-on-year growth rate of almost 114%, which is humongous.
The above figures are record-breaking and evidence enough to show a successful implementation of agency banking services in Bangladesh.
And as we know, Bangladesh was the pioneer of agency banking for financial inclusion. The latest study by the Gates Foundation on Global Findex Report 2021, it was found that, in Bangladesh, there has been a 50% increase in the use of financial services in the last decade.
Hence it is proved that Bangladesh has witnessed a positive impact of agency banking in this developing economy.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo
According to the UNCDF Report, it was found that nearly 7 million people in congo have access to formal financial services. And with the advent of agency banking, the scope of this access has increased manifold, with 25 million people still deprived of formal financial services becoming potential new customers.
The report also says there has been a significant increase in the penetration of mobile money in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). This statement indicates that the future of Congo holds extensive financial inclusion.
From all the above cases, we see that agency banking has allowed banks to reach more and more populations, which in turn has also grown the economy of these countries.
From all the above cases, we see that agency banking has allowed banks to reach more and more populations, which in turn has also grown the economy of these countries.
Want to adopt agency banking for your bank/ financial institution?
DigiPay.Guru is empowering banks to make banking services accessible to customers irrespective of their location and to expand the customer base quickly with its most reliable and convenient agency banking solution.
We aim to simplify branchless banking and make it available for all customers in unbanked or underserved areas. If you are a bank or financial institution looking to extend your banking or financial services in every location of your country, get in touch with our agency banking experts. Let us understand your needs and help you with our tailor-made solution.






