As the world moves towards a more digitally connected era, the banking sector is no exception. The emergence of digital banking has revolutionized the way we handle our finances. However, for many people in Africa, this digital revolution seems like a far-fetched dream. According to African Development Bank Report, in Africa, less than 1 adult out of 4 has access to an account at a formal financial institution.
Breaking these barriers to digital banking is crucial for the financial inclusion of Africans. And, one of the most effective ways to achieve this is through agency banking. Agency banking is a system that allows banks to offer financial services through third-party agents, such as retail stores or small businesses. This approach enables banks to expand their reach and provide banking services to unbanked populations in remote or underserved areas.
In Africa, agency banking has proven to be a game-changer in increasing financial inclusion. For instance, Equity Bank in Kenya has implemented one of the most successful agency banking programs, with over 53,151 agents serving over 15 million customers. Similarly, Ecobank in Nigeria has established a vast network of agents, reaching over 50,000 agency banking locations.
What makes agency banking particularly relevant for Africa is the high rates of financial exclusion in the region. According to the Financial Access Report of WorldBank, in Sub-Saharan Africa, 105 million adults (16 percent of adults) are unbanked. In contrast, agency banking has the potential to reach even the most remote areas, where traditional banking infrastructure is limited.
In this blog, we will delve deeper into the impact of agency banking on unbanked populations in Africa. We will explore successful agency banking programs and their benefits, including increased financial inclusion and improved access to credit, the challenges of agency banking in Africa, and potential solutions to overcome them.
Understanding the Unbanked Population
With the revolution in digital banking solutions, it's easy to take access to banking services for granted. However, the reality is that millions of people around the world lack access to even the most basic financial services. In Africa, this problem is particularly acute, with over 105 million people in Sub-Saharan Africa remaining unbanked.
The implications of this financial exclusion are far-reaching and can limit opportunities for individuals and hinder economic growth in the region. In this section, we will explore the reasons why so many people in Africa remain unbanked after so many top fintech trends in the market and the extent of financial exclusion in the region.
The Extent of Financial Exclusion in Africa
- According to the World Bank, over 60% of adults in Sub-Saharan Africa do not have a bank account.
- In some countries, such as Nigeria, this percentage is even higher, with over 70% of adults lacking access to banking services.
- Women are often disproportionately affected by financial exclusion, with only 37% of women in Sub-Saharan Africa having a bank account.
Reasons Why People Are Unbanked in Africa
- Poverty is one of the primary reasons why people in Africa remain unbanked. Without a steady income or assets to use as collateral, many people do not meet the requirements to open a bank account.
- Limited access to formal employment can also contribute to financial exclusion, as individuals may not have a consistent source of income to maintain a bank account.
- The lack of banking infrastructure in rural areas can also make it challenging for people to access banking services. In some areas, the nearest bank branch may be several hours away.
- In some cases, cultural attitudes towards banking and financial institutions may also play a role in financial exclusion.
Challenges faced by the unbanked population in accessing financial services
Access to financial services is crucial for financial inclusion and economic growth. However, for the unbanked population, accessing financial services can be a daunting task. The challenges faced by the unbanked population in accessing financial services are diverse and complex.
In Africa, these challenges are even more pronounced, with limited access to physical banking infrastructure and high costs of financial services for low-income individuals.
In this section, we will explore the challenges faced by the unbanked population in accessing financial services in Africa and discuss possible solutions.
Lack of Financial Literacy
Lack of financial literacy is a significant challenge for the unbanked population. Many individuals are not familiar with financial concepts, such as savings and credit, making it difficult for them to access financial services.
Limited access to physical banking infrastructure
Limited access to physical banking infrastructure in rural areas can pose a significant challenge for the unbanked population. In many African countries, access to financial services is limited to urban areas, leaving rural populations underserved.
High cost of financial services
Banks and financial institutions often charge high fees for financial services, making them unaffordable for low-income individuals. This can make it difficult for individuals to access credit or save money, hindering their ability to invest in their businesses or plan for the future.
Lack of identification
Many individuals do not have the necessary identification documents, such as national ID cards, to open a bank account. This can make it difficult for them to access formal financial services, as many financial institutions require proof of identity before providing services.
Limited trust in financial institutions
Many individuals have had negative experiences with financial institutions in the past, such as being charged excessive fees or experiencing fraud. This can make them hesitant to use financial services or trust financial institutions.
Language barriers
Coping with language can be challenging for the unbanked population, especially in multilingual countries. Financial institutions may not offer services in the local languages spoken by the unbanked population, making it difficult for them to understand financial concepts or access financial services.
Limited access to technology
Many financial services are now offered online. However, many individuals do not have access to the internet or smartphones, making it difficult for them to access online financial services.
To overcome these challenges, policymakers and financial institutions need to develop strategies that prioritize financial literacy, increase access to physical banking infrastructure in rural areas, reduce the cost of financial services, and promote the use of technology.
For example, Equity Bank in Kenya has established a network of agents in rural areas, allowing individuals to access financial services closer to their homes. In Nigeria, the government has launched a national identity card program to provide identification for individuals who do not have formal identification documents.
Agency Banking and its impact on the unbanked population
Agency banking is an innovative solution to expand financial inclusion and provide access to financial services for the unbanked population. This model involves using agents or third-party providers to deliver financial services on behalf of traditional banks and financial institutions.
In this section, we will explore the impact of agency banking on the unbanked population and discuss its potential to promote financial inclusion in Africa.
The Impact of Agency Banking on the Unbanked Population
Increased access to financial services
Agency banking is a top fintech solution for banks that provides an opportunity for the unbanked population to access financial services closer to their homes. Agents can be located in rural areas or other underserved communities, providing a convenient and accessible option for individuals to deposit, withdraw, or transfer money.
Reduced cost of financial services
By using agents, banks and financial institutions can reduce the cost of delivering financial services. This, in turn, can lower the cost of financial services for the unbanked population, making them more affordable and accessible.
Improved financial literacy
Agents can provide financial education and literacy to the unbanked population, helping individuals to better understand financial concepts, such as saving, budgeting, and credit. This can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions and improve their financial well-being.
Increased trust in financial institutions
By working with agents, financial institutions can build trust with the unbanked population. Agents can act as a bridge between the unbanked population and formal financial institutions, providing a more personalized and accessible experience for individuals who may have had negative experiences with traditional banks.
Boost local economies
One of the benefits of agency banking for banks is that it can stimulate local economies by providing access to financial services for small businesses and entrepreneurs. This can help to create jobs and foster economic growth in underserved communities.
How agency banking is solving the challenges faced by the unbanked population?
Agency banking has emerged as a solution to the challenges faced by the unbanked population in accessing financial services. By leveraging digital banking technologies and a network of agents, agency banking has the potential to expand financial inclusion and provide access to financial services for underserved communities.
In this section, we will explore the role of Agency Banking in solving the financial inclusion challenges faced by the unbanked population in Africa.
Increased physical presence
Agency banking has increased the physical presence of financial services in underserved communities. Agents can be located in rural areas or other underserved communities, providing a convenient and accessible option for individuals to access financial services.
Lower costs
By using agents, banks and financial institutions can reduce the cost of delivering financial services. This, in turn, can lower the cost of financial services for the unbanked population, making them more affordable and accessible.
Flexibility
Agency banking provides flexibility in accessing financial services. Agents can offer extended hours of operation and provide personalized services, such as home visits for elderly or disabled individuals.
Simplified account opening
Agency banking has simplified the process of opening a bank account. Agents can assist individuals in completing the necessary paperwork and verifying identification, making it easier for the unbanked population to access financial services.
Increased trust
By working with agents, financial institutions can build trust with the unbanked population. Agents can act as a bridge between the unbanked population and formal financial institutions, providing a more personalized and accessible experience for individuals who may have had negative experiences with traditional banks.
Convenient technology adoption
Agency banking work in a way that facilitates the adoption of convenient technology for financial transactions. Agents can use mobile devices or point-of-sale terminals to facilitate transactions, making it easier and more convenient for individuals to access financial services.
Best practices for agency banking solution providers to reach the maximum unbanked population
Agency banking has proven to be an effective solution for providing access to financial services to the unbanked population. To reach the maximum unbanked population, agency banking service providers need to follow best practices that prioritize the needs and preferences of underserved communities.
In this section, we will explore some of the best practices for agency banking solution providers to reach the maximum unbanked population, along with real-life examples from successful agency banking programs in Africa.
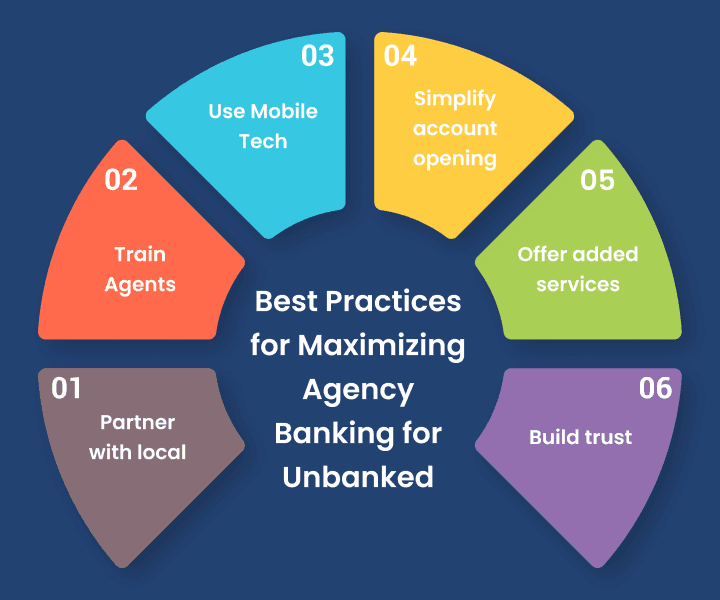
Partner with local community organizations
Partnering with local community organizations can help agency banking solution providers gain the trust and support of the community.
For example, in Uganda, Stanbic Bank partnered with local village councils to recruit and train agents from the community, resulting in increased adoption and usage of their agency banking services.
Experience the power of next-gen agency banking solutions with DigiPay.Guru
Train and empower agents
Agents play a critical role in delivering agency banking services to underserved communities. Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support to agents can help them deliver quality services and build trust with customers.
For instance, in Kenya, Equity Bank invests heavily in training and empowering its agents, resulting in high customer satisfaction and adoption rates.
Leverage mobile technology
Mobile technology can help increase the reach and efficiency of agency banking services. Mobile devices can be used by agents to facilitate transactions and access customer data, making the process of accessing financial services more convenient and accessible for underserved communities.
For example, in Nigeria, Diamond Bank leverages mobile technology to deliver agency banking services, resulting in increased adoption and usage rates.
Simplify account opening
Simplifying the account opening process can make it easier for the unbanked population to access financial services.
For instance, in Ghana, Fidelity Bank has introduced a mobile-based account opening process, allowing customers to open accounts and complete transactions through their mobile phones.
Offer value-added services
Offering value-added services, such as micro-loans or insurance products, can help agency banking solution providers differentiate themselves from traditional banks and increase customer loyalty.
For example, in Tanzania, CRDB Bank offers micro-loans and insurance products through their agency banking platform, resulting in increased customer adoption and loyalty.
Build trust
Building trust with the unbanked population is critical to the success of agency banking services. This can be achieved through transparent and ethical practices, as well as through personalized services delivered by agents.
For instance, in Zambia, Zanaco Bank has built trust with the unbanked population through their agency banking services, resulting in increased customer adoption and usage rates.
Conclusion
Agency banking has emerged as a game-changer in promoting financial inclusion in Africa. The unbanked population faces numerous challenges in accessing formal financial services, but agency banking has the potential to address these challenges by increasing physical presence, lowering costs, and simplifying account opening procedures.
Best practices for agency banking providers include partnering with local community organizations, empowering agents, leveraging mobile technology, offering value-added services, and building trust. Successful agency banking programs in Africa, such as those implemented by Equity Bank in Kenya or Ecobank in Nigeria, have followed these best practices.
By expanding agency banking in Africa, we can empower the unbanked population and drive economic growth across the continent. With DigiPay.Guru’s reliable agency banking solution, empower banks and financial institutions to make banking services and digital fintech solutions available anywhere to their customers and expand their customer base quickly.




